In React, useState Hook allows us to track state in a function component. And the state generally refers to data or properites that need to be tracking in an React application.
For the use of useState() in your React Application, you have to import useState in your react application. It does not pre import in any React Application.
import { useState } from "react";
In React, to Initialize the state by calling useState in our function component.
useState accepts an initial state and returns two values:
To Initialize the state at the top of the function component.
import { useState } from "react";
function FavoriteColor() {
const [color, setColor] = useState("");
}
we are destructuring the returned values from useState
In above, first value color is our current state. And second value setColor is the function that is use to update our state. And lastly, we set the initial state to an empty string: useState("").
We create A component FavoriteColor. And Use the state variable in the rendered component.
import { useState } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
function FavoriteColor() {
const [color, setColor] = useState("green");
return <h1>My favorite School color is {color}!</h1>
}
ReactDOM.render(<FavoriteColor />, document.getElementById('root'));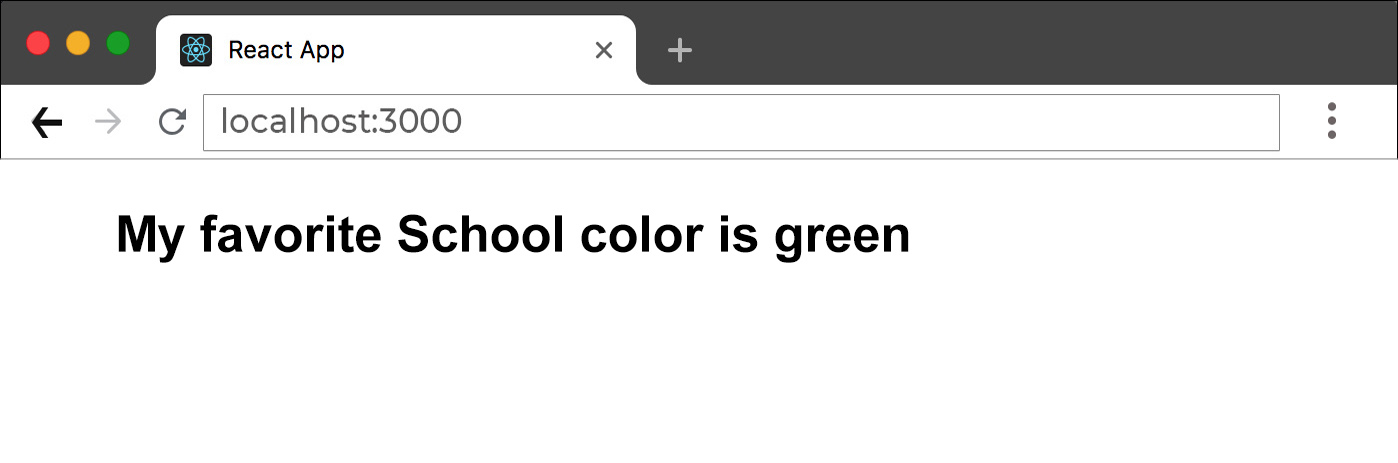
To update our state, we use our state updater function.
import { useState } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
function FavoriteColor() {
const [color, setColor] = useState("green");
return (
<>
<h1>My favorite School color is {color}!</h1>
<button
type="button"
onClick={() => setColor("red")}>
Change Color</button>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<FavoriteColor />, document.getElementById('root'));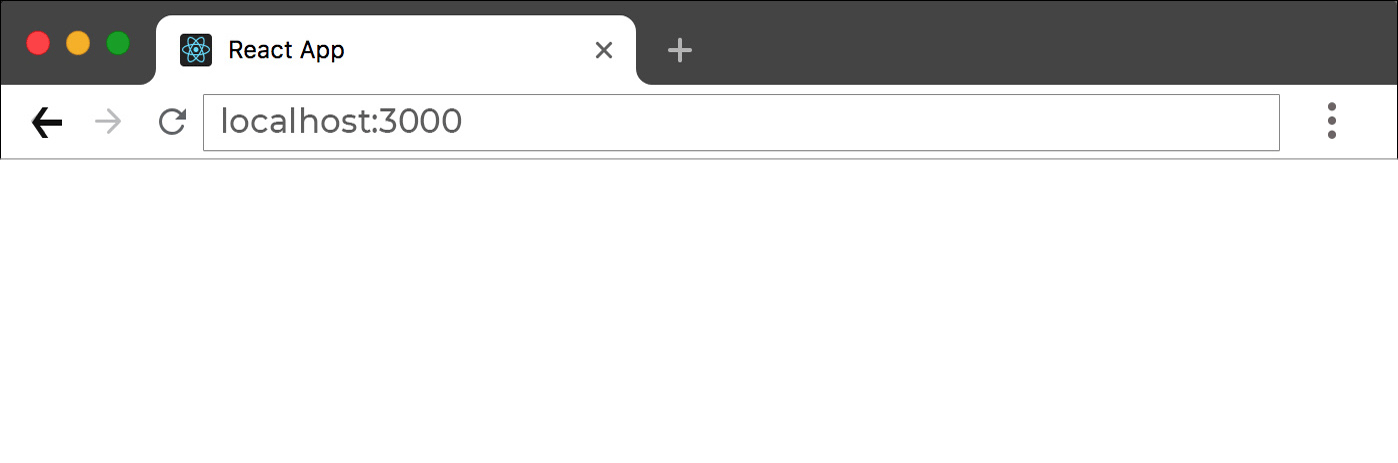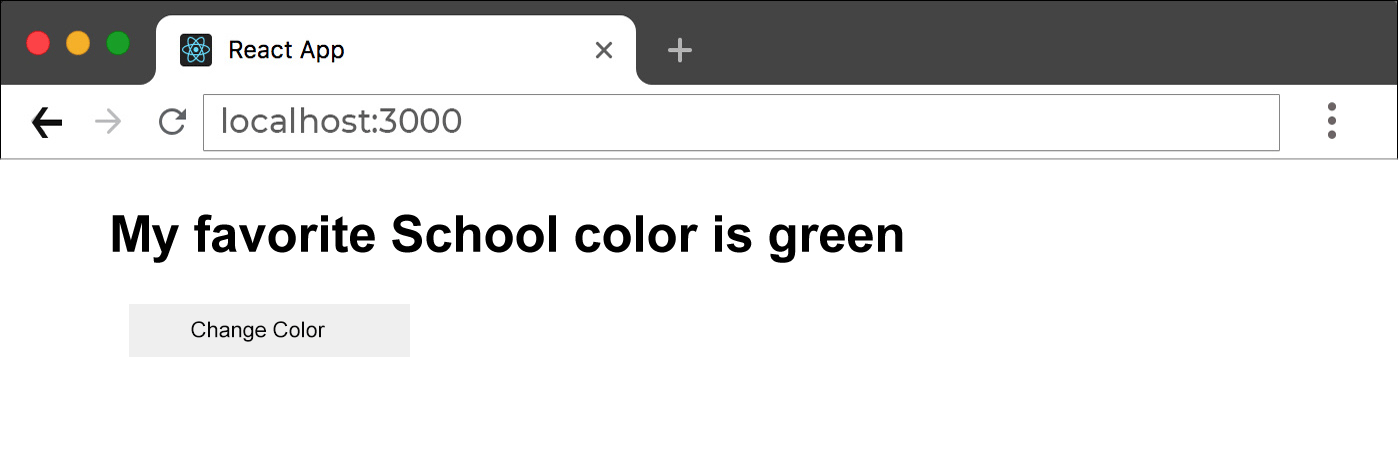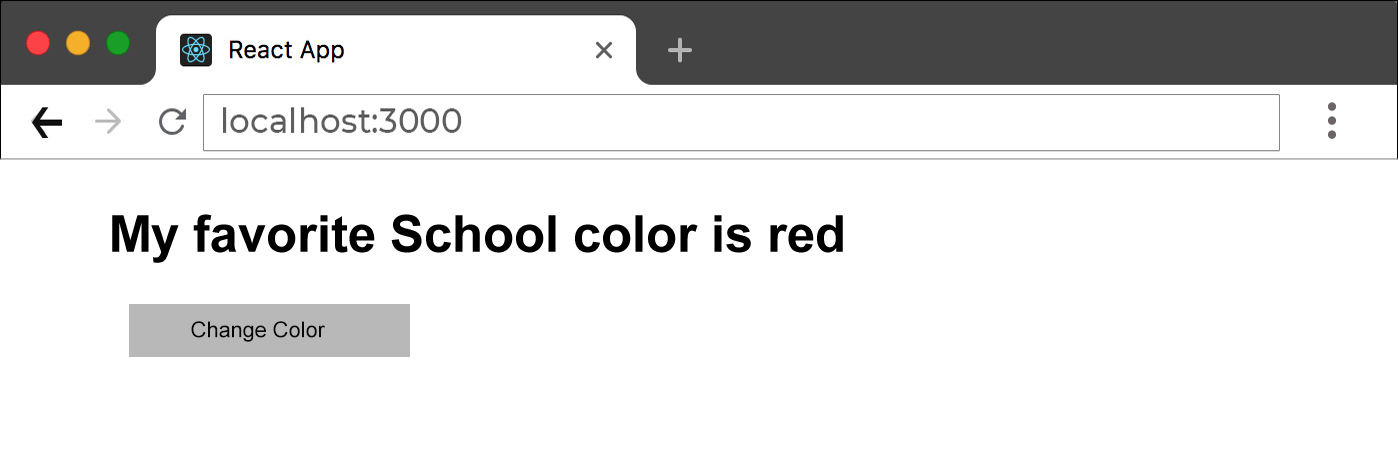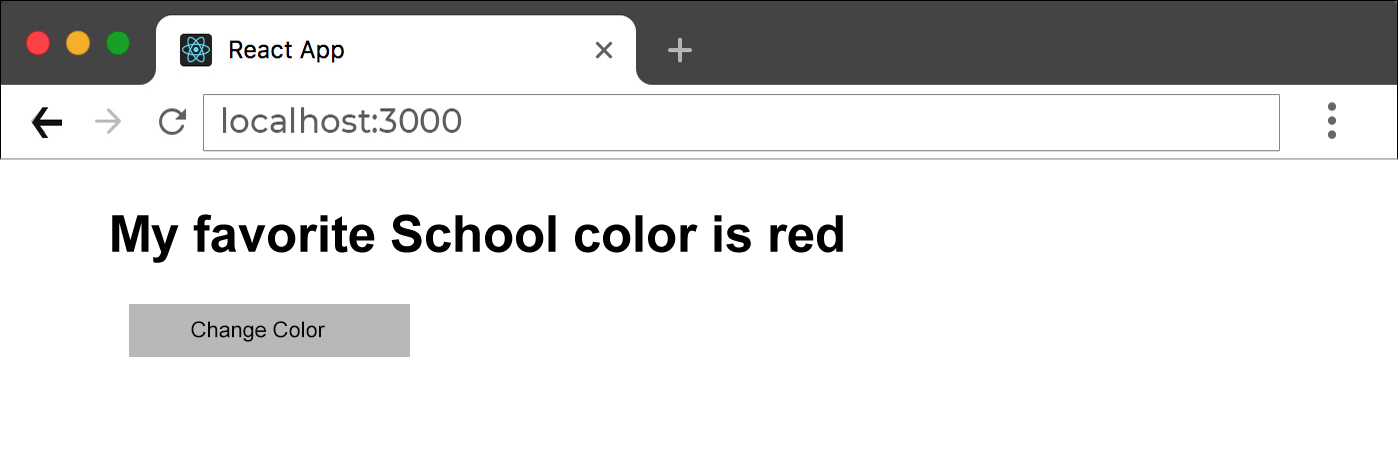
First state value color is "Green" And after click button state value update as "Red"
useState Hook can be used to keep track of strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, objects, and any combination of these!
To create multiple State Hooks to track individual values.
We create a component School with their multiple State.
import { useState } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
function School() {
const [medium, setMedium] = useState("English");
const [board, setBoard] = useState("CBSE");
const [year, setYear] = useState("1884");
const [color, setColor] = useState("green");
return (
<>
<h1>My School is {medium} Medium</h1>
<p>
It is a {color} color {board} board School from {year}.
</p>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<School />, document.getElementById('root')); 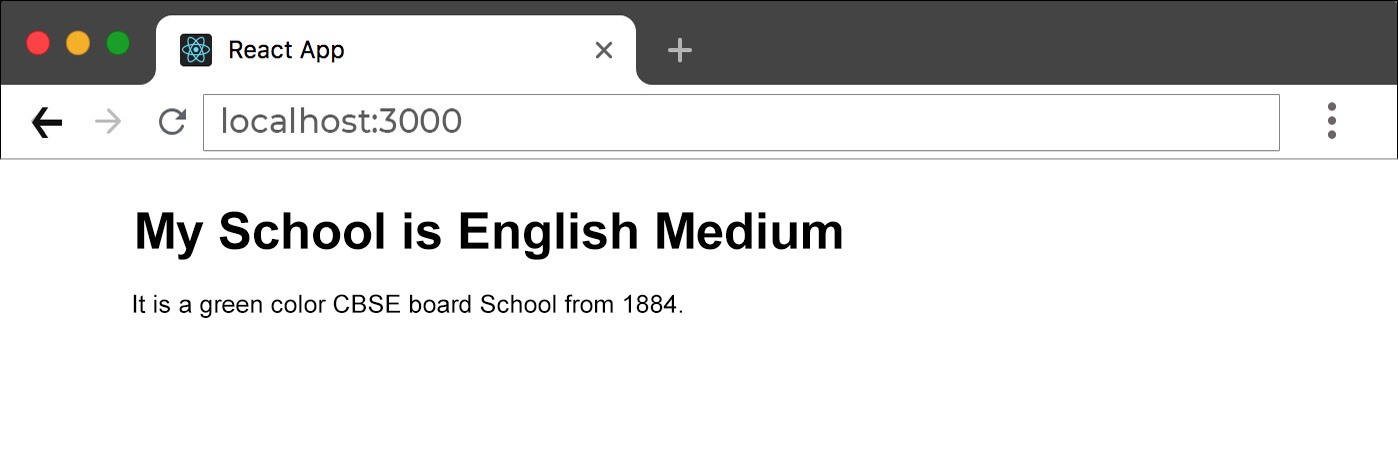
Create a single Hook that holds an object:
import { useState } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
function School() {
const [school, setSchool] = useState({
medium: "English",
board: "CBSE",
year: "1884",
color: "green"
});
return (
<>
<h1>My School is {school.medium} Medium </h1>
<p>
It is a {school.color} color {school.board} board School from {school.year}.
</p>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<School />, document.getElementById('root'));

When state is updated, the entire state gets overwritten. We will change the only color.
If we only called setSchool({color: "blue"}), this would remove the medium, board, and year from our state.
We can use the JavaScript spread operator to help us
import { useState } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
function School() {
const [school, setSchool] = useState({
medium: "English",
board: "CBSE",
year: "1884",
color: "green"
});
const updateColor = () => {
setSchool(previousState => {
return { ...previousState, color: "blue" }
});
}
return (
<>
<h1>My {school.medium} Medium </h1>
<p>
It is a {school.color} color {school.board} board from {school.year}.
</p>
<button type="button"
onClick={updateColor}
>Change Color</button>
</>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<School />, document.getElementById('root'));
We then return an object, spreading the previousState and overwriting only the color.
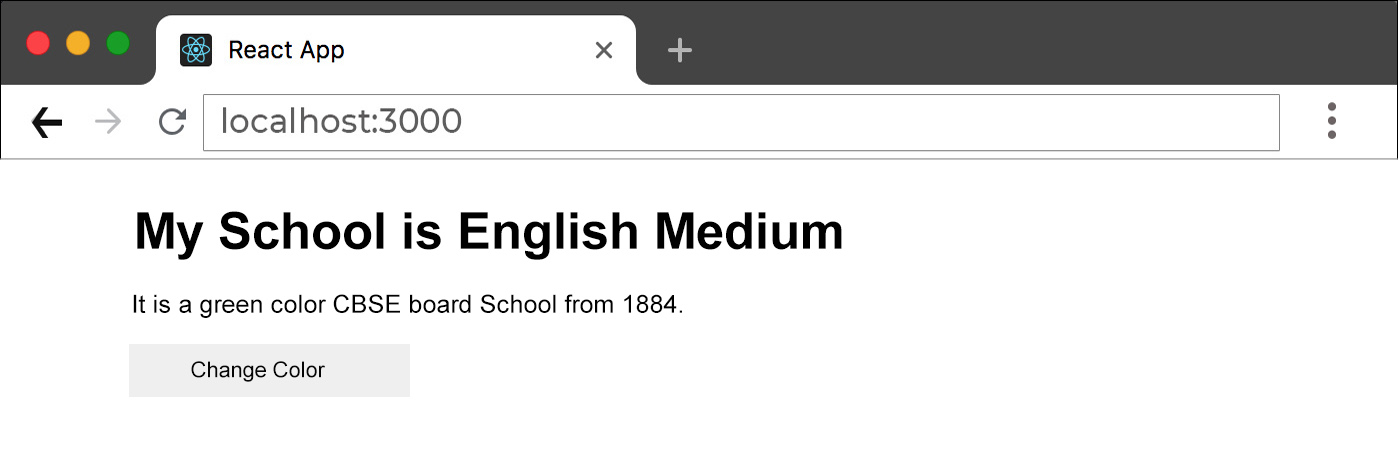
On click on button the school color will be change fron Green to Blue.
Spread syntax can be used when all elements from an object or array need to be included in a list of some kind.
Spread syntax (...) allows an iterable such as an array expression or string to be expanded in places where zero or more arguments (for function calls) or elements (for array literals) are expected, or an object expression to be expanded in places where zero or more key-value pairs (for object literals) are expected.